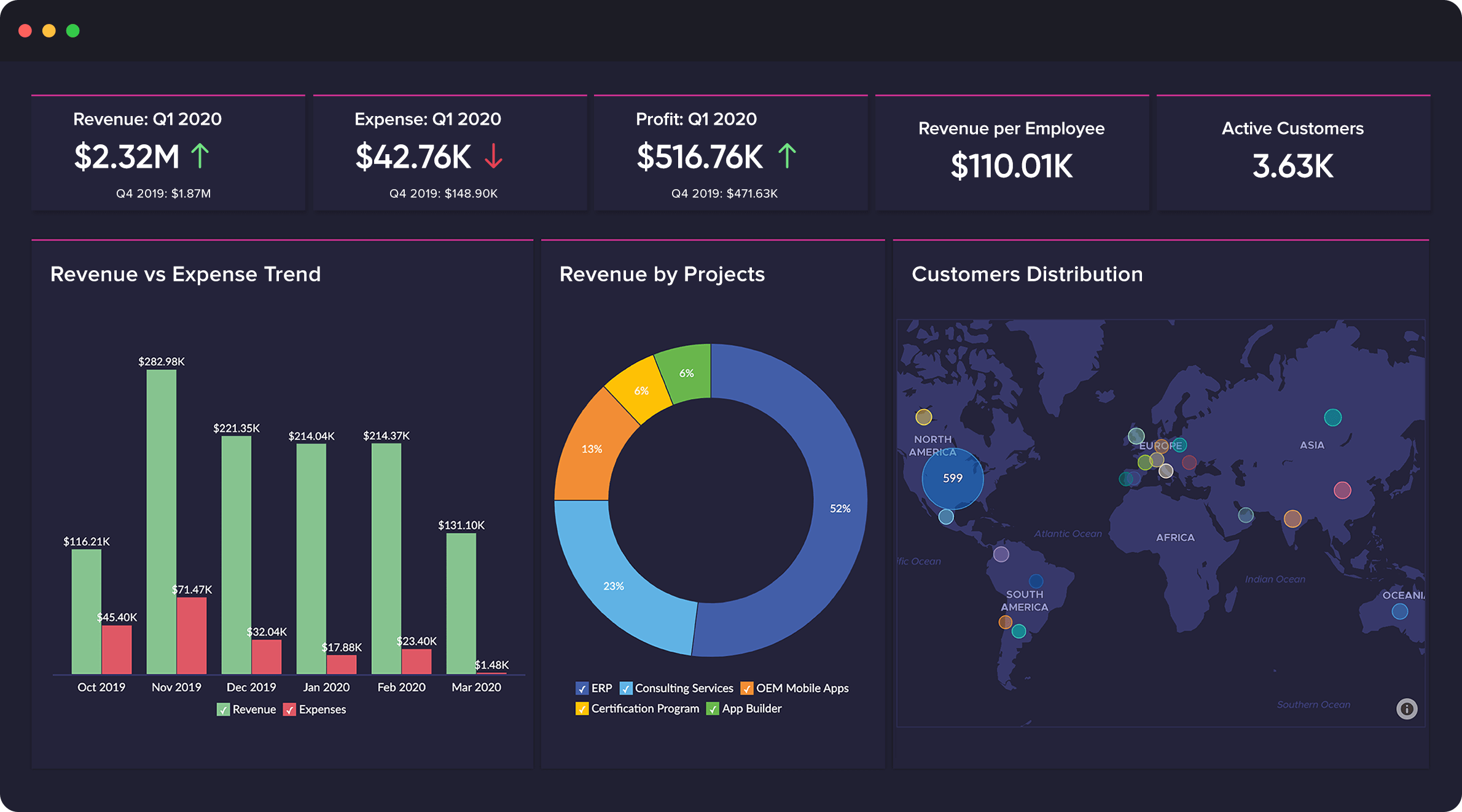
How to Implement Business Intelligence Software Successfully
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to stay ahead of the competition and make data-driven decisions. One effective way to achieve this is by implementing Business Intelligence (BI) software. BI software helps organizations to collect, analyze, and visualize data from various sources, providing valuable insights that can inform business strategies and drive growth. However, implementing BI software successfully can be a complex and challenging process. In this article, we will explore the steps to implement BI software successfully and provide tips and best practices to ensure a smooth and effective implementation.
Define Business Objectives and Requirements
Before implementing BI software, it is essential to define business objectives and requirements. This involves identifying the organization’s goals, challenges, and key performance indicators (KPIs). It is also important to determine what data is required to achieve these objectives and what type of analysis and reporting is needed. Conducting a thorough needs assessment will help to ensure that the BI software meets the organization’s specific needs and provides the required functionality.
Some key questions to consider when defining business objectives and requirements include:
- What are the organization’s key business objectives and KPIs?
- What data is required to achieve these objectives?
- What type of analysis and reporting is needed?
- Who will be using the BI software and what are their needs and requirements?
- What is the budget for the BI software implementation?
Choose the Right BI Software
With so many BI software options available, choosing the right one can be a daunting task. It is essential to evaluate different options based on the organization’s specific needs and requirements. Some key factors to consider when choosing a BI software include:
- Data sources: Can the software connect to the organization’s existing data sources, such as databases, CRM systems, and ERP systems?
- Data analysis: Does the software provide advanced data analysis capabilities, such as predictive analytics and data mining?
- Data visualization: Can the software create interactive and dynamic dashboards and reports?
- User interface: Is the software user-friendly and easy to navigate?
- Scalability: Can the software handle large volumes of data and scale to meet the organization’s growing needs?
- Integration: Can the software integrate with other systems and tools, such as Microsoft Office and Google Sheets?
Some popular BI software options include Tableau, Power BI, QlikView, and SAP BusinessObjects.
Develop a Implementation Plan
Once the BI software has been chosen, it is essential to develop a comprehensive implementation plan. This plan should outline the steps required to implement the software, including data preparation, software configuration, user training, and testing. It is also important to establish a project timeline and budget, and to identify the resources required to complete the implementation.
Some key steps to include in the implementation plan include:
- Data preparation: Cleaning, transforming, and loading data into the BI software.
- Software configuration: Configuring the software to meet the organization’s specific needs and requirements.
- User training: Providing training and support to users to ensure they can effectively use the software.
- Testing: Testing the software to ensure it is functioning correctly and meeting the organization’s needs.
- Deployment: Deploying the software to production and making it available to users.
Data Preparation
Data preparation is a critical step in the BI software implementation process. This involves cleaning, transforming, and loading data into the BI software. It is essential to ensure that the data is accurate, complete, and consistent, and that it is in a format that can be easily analyzed and visualized.
Some key data preparation tasks include:
- Data cleaning: Removing duplicate or inaccurate data, and handling missing values.
- Data transformation: Transforming data into a format that can be easily analyzed and visualized.
- Data loading: Loading data into the BI software, such as databases or data warehouses.
Software Configuration
Software configuration involves setting up the BI software to meet the organization’s specific needs and requirements. This includes configuring the software’s data connections, data models, and security settings.
Some key software configuration tasks include:
- Data connections: Configuring the software to connect to the organization’s data sources, such as databases and CRM systems.
- Data models: Creating data models that reflect the organization’s business processes and metrics.
- Security settings: Configuring the software’s security settings to ensure that only authorized users can access the data and analytics.
User Training and Support
Providing user training and support is essential to ensure that users can effectively use the BI software and achieve the organization’s business objectives. This includes providing training sessions, user documentation, and online support resources.
Some key user training and support tasks include:
- Training sessions: Providing training sessions to users to teach them how to use the software and create reports and dashboards.
- User documentation: Creating user documentation, such as user guides and tutorials, to help users get started with the software.
- Online support: Providing online support resources, such as FAQs and forums, to help users troubleshoot issues and get answers to their questions.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing and quality assurance are critical steps in the BI software implementation process. This involves testing the software to ensure it is functioning correctly and meeting the organization’s needs, and conducting quality assurance activities to ensure the data and analytics are accurate and reliable.
Some key testing and quality assurance tasks include:
- Software testing: Testing the software to ensure it is functioning correctly and meeting the organization’s needs.
- Data testing: Testing the data to ensure it is accurate, complete, and consistent.
- Quality assurance: Conducting quality assurance activities to ensure the data and analytics are accurate and reliable.
Deployment and Maintenance
Once the BI software has been implemented, it is essential to deploy it to production and make it available to users. This involves setting up the software’s infrastructure, configuring the software’s security settings, and providing ongoing maintenance and support.
Some key deployment and maintenance tasks include:
- Infrastructure setup: Setting up the software’s infrastructure, such as servers and databases.
- Security settings: Configuring the software’s security settings to ensure that only authorized users can access the data and analytics.
- Ongoing maintenance: Providing ongoing maintenance and support to ensure the software continues to function correctly and meet the organization’s needs.
Conclusion
Implementing BI software successfully requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance. By following the steps outlined in this article, organizations can ensure a smooth and effective implementation and achieve their business objectives. Remember to define business objectives and requirements, choose the right BI software, develop a comprehensive implementation plan, prepare data, configure the software, provide user training and support, test and quality assure, and deploy and maintain the software. With the right approach and tools, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data and drive business success.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into How to Implement Business Intelligence Software Successfully. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!